Describe How a Substrate Interacts With an Enzyme
Competitive noncompetitive and uncompetitive. Lipases for example help digest fat.
For example 5---TTACGnnnnnn CGTAA---3 is an inverted repeat sequence.

. This interface which is also found in TIR domain. This enzyme thus provides an exciting platform for additional protein engineering and evolution to increase the efficiency and substrate range of this polyesterase as well as to provide clues of how to further engineer thermophilic cutinases to better incorporate aromatic polyesters toward to the persistent challenge of highly crystalline polymer degradation. There is great interest in developing SARM1 enzyme inhibitors as candidate therapies for.
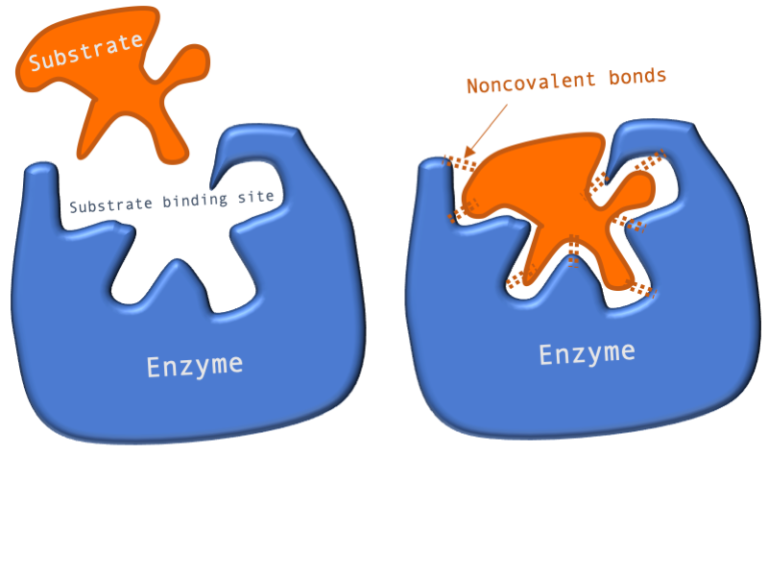
A similar shape exists between a pocket on the surface of the enzyme and a functional group on the substrate. A nonspecific inhibition effects all enzymes in the. A water molecule bridges the side chain of serine from the substrate to the main chain of A41 through hydrogen bonds which may account for serine being frequently observed at this site SI Appendix Fig.
List the characteristics originally used to describe prokaryotic cells 2. There are a variety of types of inhibitors including. Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the body.
Form an opinion on the prokaryote controversy using current evidence about bacterial cells 2. They affect every function from breathing to digestion. Distinguish a typical bacterial cell from a typical plant or animal cell in terms of cell shapes and arrangements size and cell structures 2.
S7 A B D and E. The enzyme has an allosteric regulatory site. Competitive inhibition happens when a compound similar to the substrate is present and competes with the substrate for the active sites of the enzyme obstructing the access of substrate to the active site thus slowing down the reaction.
An inverted repeat or IR is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. Poisons and drugs are examples of enzyme inhibitors. When the intervening length is zero the composite.
The side chain at P1 also interacts with the side chains of T25 L27 and C145 through van der Waals interactions. And the structure revealed an unusual orthosteric site in which 1AD interacts with both chains defined here as hSARM1 TIR-A and hSARM1 TIR-B of the asymmetric BB-loop mediated interface Figures 2A and 2B. A hydrophobic group on the substrate interacts with several hydrophobic amino acids on the enzyme.
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that interact in some way with the enzyme to prevent it from working in the normal manner. Enzyme inhibition can be categorized in three types. The primary end point of this study was the effects of 12 weeks of G cambogia extract administration on visceral fat accumulation.
The mitochondrial unfolded protein response UPR mt has emerged as a predominant mechanism that preserves mitochondrial functionConsequently multiple pathways likely exist to modulate UPR mtWe discovered that the tRNA processing enzyme homolog of ELAC2 HOE-1 is key to UPR mt regulation in Caenorhabditis elegansWe find that nuclear. The secondary end points were body indices including height body weight body mass index BMI waist and hip circumference and waisthip ratio and laboratory values including total cholesterol triacylglycerol and free fatty acid. Nonspecific irreversible reversible - competitive and noncompetitive.
This gene encodes a glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the addition of a single N-acetylglucosamine in O-glycosidic linkage to serine or threonine residues. Discuss the factors that determine the size. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero.
A positive charge on the substrate is attracted to a negative charge in the active site of the enzyme. 32 A Typical Bacterial Cell 1. Since both phosphorylation and glycosylation compete for similar serine or threonine residues the two processes may compete for sites or they may alter the substrate specificity of nearby sites by.
Biology Toolbox Enzyme Substrate Interactions And Inhibition

2 7 2 Enzyme Active Site And Substrate Specificity Biology Libretexts

Principles Of Biochemistry Enzymes Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

No comments for "Describe How a Substrate Interacts With an Enzyme"
Post a Comment